Cluster Deployment¶
Tip
Since version 8.0, the recommend way to install Seafile clsuter is using Docker
Cluster requirements¶
Please refer here for the details about the cluster requirements for all nodes in Seafile cluster. In general, we recommend that each node should have at least 2G RAM and a 2-core CPU (> 2GHz).
Preparation (all nodes)¶
Install prerequisites¶
Please follow here to install prerequisites
Note
Cache server (the first step) is not necessary, if you donot wish this node deploy it.
Create user seafile¶
Create a new user and follow the instructions on the screen:
adduser seafile
Change ownership of the created directory to the new user:
chown -R seafile: /opt/seafile
All the following steps are done as user seafile.
Change to user seafile:
su seafile
Placing the Seafile PE license in /opt/seafile¶
Save the license file in Seafile's programm directory /opt/seafile. Make sure that the name is seafile-license.txt.
If the license file has a different name or cannot be read, Seafile server will start with in trailer mode with most THREE users
Setup and configure Nginx (only for frontend nodes)¶
For security reasons, the Seafile frontend service will only listen to requests from the local port 8000. You need to use Nginx to reverse proxy this port to port 80 for external access:
-
Install Nginx
sudo apt update sudo apt install nginx -
Create the configurations file for current node
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/seafile.confand, add the following contents into this file:
log_format seafileformat '$http_x_forwarded_for $remote_addr [$time_local] "$request" $status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" "$http_user_agent" $upstream_response_time'; server { listen 80; server_name <current node's IP>; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr; location / { proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8000; proxy_set_header Host $http_host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $server_name; proxy_read_timeout 1200s; # used for view/edit office file via Office Online Server client_max_body_size 0; access_log /var/log/nginx/seahub.access.log seafileformat; error_log /var/log/nginx/seahub.error.log; } location /seafhttp { rewrite ^/seafhttp(.*)$ $1 break; proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8082; client_max_body_size 0; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_read_timeout 36000s; proxy_send_timeout 36000s; send_timeout 36000s; access_log /var/log/nginx/seafhttp.access.log seafileformat; error_log /var/log/nginx/seafhttp.error.log; } location /media { root /opt/seafile/seafile-server-latest/seahub; } } -
Link the configurations file to
sites-enableddirectory:sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/seafile.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ -
Test and enable configuration
sudo nginx -t sudo nginx -s reload
Start Seafile Service on boot (optional)¶
It would be convenient to setup Seafile service to start on system boot. Follow this documentation to set it up on.
Firewall Settings¶
There are 2 firewall rule changes for Seafile cluster:
- On each nodes, you should open the health check port (default 11001);
- On the Cache and ElasticSearch server, please only allow Seafile servers to access this port for security resons.
Setup the first frontend Node¶
Setup Seafile server Pro¶
Please follow Installation of Seafile Server Professional Edition to setup:
Create and Modify configuration files in /opt/seafile/conf¶
.env¶
Tip
JWT_PRIVATE_KEY, A random string with a length of no less than 32 characters can be generated from:
pwgen -s 40 1
JWT_PRIVATE_KEY=<Your jwt private key>
SEAFILE_SERVER_PROTOCOL=https
SEAFILE_SERVER_HOSTNAME=seafile.example.com
SEAFILE_MYSQL_DB_HOST=<your database host>
SEAFILE_MYSQL_DB_PORT=3306
SEAFILE_MYSQL_DB_USER=seafile
SEAFILE_MYSQL_DB_PASSWORD=<your MySQL password>
SEAFILE_MYSQL_DB_CCNET_DB_NAME=ccnet_db
SEAFILE_MYSQL_DB_SEAFILE_DB_NAME=seafile_db
SEAFILE_MYSQL_DB_SEAHUB_DB_NAME=seahub_db
seafile.conf¶
-
Add or modify the following configuration to
seafile.conf:[memcached] memcached_options = --SERVER=<your memcached ip>[:<your memcached port>] --POOL-MIN=10 --POOL-MAX=100[redis] redis_host = <your redis ip> redis_port = <your redis port, default 6379> max_connections = 100 -
Enable cluster mode
[cluster] enabled = trueMore options in
clustersectionThe Seafile server also opens a port for the load balancers to run health checks. Seafile by default uses port
11001. You can change this by adding the following config:[cluster] health_check_port = 12345 -
Enable backend storage:
seahub_settings.py¶
-
You must setup and use memory cache when deploying Seafile cluster, please add or modify the following configuration to
seahub_settings.py:CACHES = { 'default': { 'BACKEND': 'django_pylibmc.memcached.PyLibMCCache', 'LOCATION': '<your Memcached host>:<your Memcached port, default 11211>', }, }please Refer to Django's documentation about using Redis cache to add Redis configurations to
seahub_settings.py. -
Add following options to seahub_setting.py, which will tell Seahub to store avatar in database and cache avatar in memcached, and store css CACHE to local memory.
AVATAR_FILE_STORAGE = 'seahub.base.database_storage.DatabaseStorage'
seafevents.conf¶
Modify the [INDEX FILES] section to enable full test search, we take ElasticSearch for example:
[INDEX FILES]
enabled = true
interval = 10m
highlight = fvh
index_office_pdf = true
es_host = <your ElasticSearch host>
es_port = <your ElasticSearch port, default 9200>
Update Seahub Database¶
In cluster environment, we have to store avatars in the database instead of in a local disk.
mysql -h<your MySQL host> -P<your MySQL port> -useafile -p<user seafile's password>
# enter MySQL environment
USE seahub_db;
CREATE TABLE `avatar_uploaded` (`filename` TEXT NOT NULL, `filename_md5` CHAR(32) NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY, `data` MEDIUMTEXT NOT NULL, `size` INTEGER NOT NULL, `mtime` datetime NOT NULL);
Run and Test the Single Node¶
Once you have finished configuring this single node, start it to test if it runs properly:
Note
For installations using python virtual environment, activate it if it isn't already active
source python-venv/bin/activate
cd /opt/seafile/seafile-server-latest
su seafile
./seafile.sh start
./seahub.sh start
Success
The first time you start seahub, the script would prompt you to create an admin account for your Seafile server. Then you can see the following message in your console:
Starting seafile server, please wait ...
Seafile server started
Done.
Starting seahub at port 8000 ...
Seahub is started
Done.
Finally, you can visit http://ip-address-of-this-node:80 and login with the admin account to test if this node is working fine or not.
Configure other frontend nodes¶
If the first frontend node works fine, you can compress the whole directory /opt/seafile into a tarball and copy it to all other Seafile server nodes. You can simply uncompress it and start the server by:
Note
For installations using python virtual environment, activate it if it isn't already active
source python-venv/bin/activate
cd /opt/seafile/seafile-server-latest
su seafile
./seafile.sh start
./seahub.sh start
Backend node¶
In the backend node, you need to execute the following command to start Seafile server. CLUSTER_MODE=backend means this node is seafile backend server.
Note
For installations using python virtual environment, activate it if it isn't already active
source python-venv/bin/activate
export CLUSTER_MODE=backend
cd /opt/seafile/seafile-server-latest
su seafile
./seafile.sh start
./seafile-background-tasks.sh start
Load Balancer Setting¶
Note
Since Seafile Pro server 6.0.0, cluster deployment requires "sticky session" settings in the load balancer. Otherwise sometimes folder download on the web UI can't work properly. Read the "Load Balancer Setting" section below for details
Generally speaking, in order to better access the Seafile service, we recommend that you use a load balancing service to access the Seafile cluster and bind your domain name (such as seafile.cluster.com) to the load balancing service. Usually, you can use:
- Cloud service provider's load balancing service (e.g., AWS Elastic Load Balancer)
-
Deploy your own load balancing service, our document will give two of common load balance services:
- Nginx
- HAproxy
AWS Elastic Load Balancer (ELB)¶
In the AWS ELB management console, after you've added the Seafile server instances to the instance list, you should do two more configurations.
First you should setup HTTP(S) listeners. Ports 443 and 80 of ELB should be forwarded to the ports 80 or 443 of the Seafile servers.
Then you setup health check
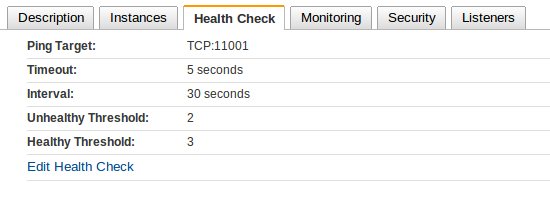
Refer to AWS documentation about how to setup sticky sessions.
Nginx¶
-
Install Nginx in the host if you would like to deploy load balance service
sudo apt update sudo apt install nginx -
Create the configurations file for Seafile cluster
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/seafile-clusterand, add the following contents into this file:
upstream seafile_cluster { server <IP: your frontend node 1>:80; server <IP: your frontend node 2>:80; ... } server { listen 80; server_name <your domain>; location / { proxy_pass http://seafile_cluster; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; proxy_next_upstream error timeout invalid_header http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504; proxy_next_upstream_tries 3; client_max_body_size 0; } } -
Link the configurations file to
sites-enableddirectory:sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/seafile-cluster /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ -
Test and enable configuration
sudo nginx -t sudo nginx -s reload
HAProxy¶
This is a sample /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg:
(Assume your health check port is 11001)
global
log 127.0.0.1 local1 notice
maxconn 4096
user haproxy
group haproxy
defaults
log global
mode http
retries 3
maxconn 2000
timeout connect 10000
timeout client 300000
timeout server 36000000
listen seafile 0.0.0.0:80
mode http
option httplog
option dontlognull
option forwardfor
cookie SERVERID insert indirect nocache
server seafileserver01 192.168.1.165:80 check port 11001 cookie seafileserver01
server seafileserver02 192.168.1.200:80 check port 11001 cookie seafileserver02
See how it runs¶
Now you should be able to test your cluster. Open https://seafile.example.com in your browser and enjoy. You can also synchronize files with Seafile clients.
The final configuration of the front-end nodes¶
Here is the summary of configurations at the front-end node that related to cluster setup. (for version 7.1+)
For seafile.conf:
[cluster]
enabled = true
The enabled option will prevent the start of background tasks by ./seafile.sh start in the front-end node. The tasks should be explicitly started by ./seafile-background-tasks.sh start at the back-end node.
For seahub_settings.py:
AVATAR_FILE_STORAGE = 'seahub.base.database_storage.DatabaseStorage'
For seafevents.conf:
[INDEX FILES]
enabled = true
interval = 10m
highlight = fvh # This configuration is for improving searching speed
es_host = <IP of background node>
es_port = 9200
The [INDEX FILES] section is needed to let the front-end node know the file search feature is enabled.
HTTPS¶
You can engaged HTTPS in your load balance service, as you can use certificates manager (e.g., Certbot) to acquire and enable HTTPS to your Seafile cluster. You have to modify the relative URLs from the prefix http:// to https:// in seahub_settings.py and .env, after enabling HTTPS.
(Optional) Deploy SeaDoc server¶
You can follow here to deploy SeaDoc server. And then modify SEADOC_SERVER_URL in your .env file