Distributed indexing¶
If you use a cluster to deploy Seafile, you can use distributed indexing to realize real-time indexing and improve indexing efficiency. The indexing process is as follows:
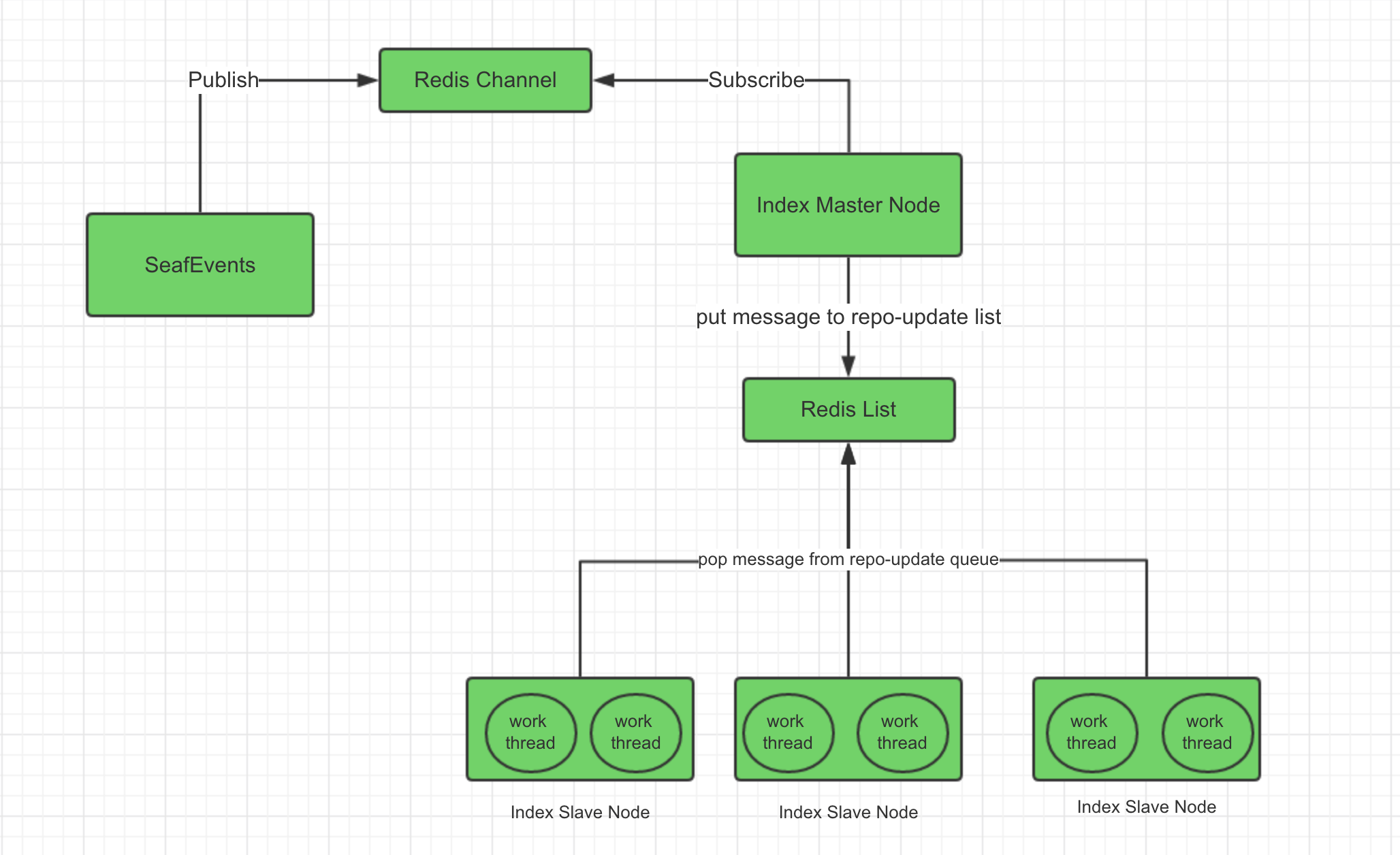
Install redis and modify configuration files¶
1. Install redis on all frontend nodes¶
Tip
If you use redis cloud service, skip this step and modify the configuration files directly
$ apt install redis-server
$ yum install redis
2. Install python redis third-party package on all frontend nodes¶
$ pip install redis
3. Modify the seafevents.conf on all frontend nodes¶
Add the following config items
[EVENTS PUBLISH]
mq_type=redis # must be redis
enabled=true
[REDIS]
server=127.0.0.1 # your redis server host
port=6379 # your redis server port
password=xxx # your redis server password, if not password, do not set this item
4. Modify the seafevents.conf on the backend node¶
Disable the scheduled indexing task, because the scheduled indexing task and the distributed indexing task conflict.
[INDEX FILES]
enabled=true
|
V
enabled=false
5. Restart Seafile¶
docker exec -it seafile bash
cd /scripts
./seafile.sh restart && ./seahub.sh restart
cd /opt/seafile/seafile-server-latest
./seafile.sh restart && ./seahub.sh restart
Deploy distributed indexing¶
First, prepare a index-server master node and several index-server slave nodes, the number of slave nodes depends on your needs. Copy the seafile.conf and the seafevents.conf in the conf directory from the Seafile frontend nodes to /opt/seafile-data/seafile/conf in index-server nodes. The master node and slave nodes need to read the configuration files to obtain the necessary information.
mkdir -p /opt/seafile-data/seafile/conf
mkdir -p /opt/seafile
Then download .env and index-server.yml to /opt/seafile in all index-server nodes.
cd /opt/seafile
wget https://manual.seafile.com/12.0/repo/docker/index-server/index-server.yml
wget -O .env https://manual.seafile.com/12.0/repo/docker/index-server/env
Modify mysql configurations in .env.
SEAFILE_MYSQL_DB_HOST=127.0.0.1
SEAFILE_MYSQL_DB_PORT=3306
SEAFILE_MYSQL_DB_USER=seafile
SEAFILE_MYSQL_DB_PASSWORD=PASSWORD
CLUSTER_MODE=master
Note
CLUSTER_MODE needs to be configured as master on the master node, and needs to be configured as worker on the slave nodes.
Next, create a configuration file index-master.conf in the conf directory of the master node, e.g.
[DEFAULT]
mq_type=redis # must be redis
[REDIS]
server=127.0.0.1 # your redis server host
port=6379 # your redis server port
password=xxx # your redis server password, if not password, do not set this item
Start master node.
docker compose up -d
Next, create a configuration file index-worker.conf in the conf directory of all slave nodes, e.g.
[DEFAULT]
mq_type=redis # must be redis
index_workers=2 # number of threads to create/update indexes, you can increase this value according to your needs
[REDIS]
server=127.0.0.1 # your redis server host
port=6379 # your redis server port
password=xxx # your redis server password, if not password, do not set this item
Start all slave nodes.
docker compose up -d
Some commands in distributed indexing¶
Rebuild search index, first execute the command in the Seafile node:
cd /opt/seafile/seafile-server-last/
./pro/pro.py search --clear
Then execute the command in the index-server master node:
docker exec -it index-server bash
/opt/seafile/index-server/index-server.sh restore-all-repo
List the number of indexing tasks currently remaining, execute the command in the index-server master node:
/opt/seafile/index-server/index-server.sh show-all-task