Installation of Seafile Server Professional Edition¶
This manual explains how to deploy and run Seafile Server Professional Edition (Seafile PE) on a Linux server from a pre-built package using MySQL/MariaDB as database. The deployment has been tested for Debian/Ubuntu.
Requirements¶
Please refer here for system requirements about Seafile PE. In general, we recommend that you should have at least 4G RAM and a 4-core CPU (> 2GHz).
Seafile PE can be used without a paid license with up to three users. Licenses for more user can be purchased in the Seafile Customer Center or contact Seafile Sales at sales@seafile.com or one of our partners.
Setup¶
Installing and preparing the SQL database¶
Seafile supports MySQL and MariaDB. We recommend that you use the preferred SQL database management engine included in the package repositories of your distribution.
You can find step-by-step how-tos for installing MySQL and MariaDB in the tutorials on the Digital Ocean website.
Seafile uses the mysql_native_password plugin for authentication. The versions of MySQL and MariaDB installed on CentOS 8, Debian 10, and Ubuntu 20.04 use a different authentication plugin by default. It is therefore required to change to authentication plugin to mysql_native_password for the root user prior to the installation of Seafile. The above mentioned tutorials explain how to do it.
Installing prerequisites¶
Tip
The standard directory /opt/seafile is assumed for the rest of this manual. If you decide to put Seafile in another directory, some commands need to be modified accordingly
-
Install cache server (e.g., Memcached)
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install -y memcached libmemcached-dev -
Install Python and related libraries
Note
Debian 12 and Ubuntu 24.04 are now discouraging system-wide installation of python modules with pip. It is preferred now to install modules into a virtual environment which keeps them separate from the files installed by the system package manager, and enables different versions to be installed for different applications. With these python virtual environments (venv for short) to work, you have to activate the venv to make the packages installed in it available to the programs you run. That is done here with
source python-venv/bin/activate.sudo apt-get install -y python3 python3-dev python3-setuptools python3-pip libmysqlclient-dev ldap-utils libldap2-dev python3.12-venv default-libmysqlclient-dev build-essential pkg-config libmemcached-dev mkdir /opt/seafile cd /opt/seafile # create the vitual environment in the python-venv directory python3 -m venv python-venv # activate the venv source python-venv/bin/activate # Notice that this will usually change your prompt so you know the venv is active # install packages into the active venv with pip (sudo isn't needed because this is installing in the venv, not system-wide). pip3 install --timeout=3600 django==4.2.* future==1.0.* mysqlclient==2.2.* \ pymysql pillow==10.4.* pylibmc captcha==0.6.* markupsafe==2.0.1 jinja2 sqlalchemy==2.0.* \ psd-tools django-pylibmc django_simple_captcha==0.6.* djangosaml2==1.9.* pysaml2==7.3.* pycryptodome==3.20.* cffi==1.17.0 lxml python-ldap==3.4.* gevent==24.2.*Note
Debian 12 and Ubuntu 24.04 are now discouraging system-wide installation of python modules with pip. It is preferred now to install modules into a virtual environment which keeps them separate from the files installed by the system package manager, and enables different versions to be installed for different applications. With these python virtual environments (venv for short) to work, you have to activate the venv to make the packages installed in it available to the programs you run. That is done here with
source python-venv/bin/activate.sudo apt-get install -y python3 python3-dev python3-setuptools python3-pip libmariadb-dev-compat ldap-utils libldap2-dev libsasl2-dev python3.11-venv mkdir /opt/seafile cd /opt/seafile # create the vitual environment in the python-venv directory python3 -m venv python-venv # activate the venv source python-venv/bin/activate # Notice that this will usually change your prompt so you know the venv is active # install packages into the active venv with pip (sudo isn't needed because this is installing in the venv, not system-wide). pip3 install --timeout=3600 django==4.2.* future==0.18.* mysqlclient==2.1.* pymysql pillow==10.0.* pylibmc captcha==0.4 markupsafe==2.0.1 jinja2 sqlalchemy==2.0.18 psd-tools django-pylibmc django_simple_captcha==0.5.* djangosaml2==1.5.* pysaml2==7.2.* pycryptodome==3.16.* cffi==1.15.1 lxml python-ldap==3.4.3sudo apt-get install -y python3 python3-dev python3-setuptools python3-pip libmysqlclient-dev ldap-utils libldap2-dev default-libmysqlclient-dev build-essential pkg-config libmemcached-dev sudo mkdir /opt/seafile cd /opt/seafile sudo pip3 install --timeout=3600 django==4.2.* future==1.0.* mysqlclient==2.1.* \ pymysql pillow==10.4.* pylibmc captcha==0.6.* markupsafe==2.0.1 jinja2 sqlalchemy==2.0.* \ psd-tools django-pylibmc django_simple_captcha==0.6.* djangosaml2==1.9.* pysaml2==7.2.* pycryptodome==3.16.* cffi==1.15.1 python-ldap==3.2.0 lxml gevent==24.2.*sudo apt-get install -y python3 python3-dev python3-setuptools python3-pip libmysqlclient-dev-compat ldap-utils libldap2-dev libsasl2-dev sudo mkdir /opt/seafile cd /opt/seafile sudo pip3 install --timeout=3600 django==4.2.* future==1.0.* mysqlclient==2.2.* \ pymysql pillow==10.4.* pylibmc captcha==0.6.* markupsafe==2.0.1 jinja2 sqlalchemy==2.0.* \ psd-tools django-pylibmc django_simple_captcha==0.6.* djangosaml2==1.9.* pysaml2==7.2.* pycryptodome==3.16.* cffi==1.15.1 python-ldap==3.2.0 lxml gevent==24.2.*sudo dnf --enablerepo=crb install -y mysql-devel libmemcached-awesome libmemcached-awesome-devel && sudo dnf install -y gcc python3.12 python3.12-devel python3.12-pip python3.12-setuptools python3-devel python3-ldap openldap-devel libffi-devel mkdir /opt/seafile cd /opt/seafile # create the vitual environment in the python-venv directory python3.12 -m venv python-venv # activate the venv source python-venv/bin/activate # Notice that this will usually change your prompt so you know the venv is active # install packages into the active venv with pip (sudo isn't needed because this is installing in the venv, not system-wide). pip3 install --timeout=3600 django==4.2.* future==0.18.* mysqlclient==2.1.* pymysql pillow==10.0.* pylibmc captcha==0.4 markupsafe==2.0.1 jinja2 sqlalchemy==2.0.18 psd-tools django-pylibmc django_simple_captcha==0.5.* djangosaml2==1.5.* pysaml2==7.2.* pycryptodome==3.16.* cffi==1.15.1 lxml python-ldap==3.4.3
Creating user seafile¶
Elasticsearch, the indexing server, cannot be run as root. More generally, it is good practice not to run applications as root.
Create a new user and follow the instructions on the screen:
adduser seafile
/usr/sbin/adduser seafile
adduser seafile
Change ownership of the created directory to the new user:
chown -R seafile: /opt/seafile
All the following steps are done as user seafile.
Change to user seafile:
su seafile
Placing the Seafile PE license¶
Save the license file in Seafile's programm directory /opt/seafile. Make sure that the name is seafile-license.txt.
If the license file has a different name or cannot be read, Seafile server will start with in trailer mode with most THREE users
Downloading the install package¶
The install packages for Seafile PE are available for download in the the Seafile Customer Center. To access the Customer Center, a user account is necessary. The registration is free.
Beginning with Seafile PE 7.0.17, the Seafile Customer Center provides two install packages for every version (using Seafile PE 12.0.6 as an example):
- seafile-pro-server_12.0.6_x86-64_Ubuntu.tar.gz, compiled in Ubuntu environment
The former is suitable for installation on Ubuntu/Debian servers.
Download the install package using wget (replace the x.x.x with the version you wish to download):
# Debian/Ubuntu
wget -O 'seafile-pro-server_x.x.x_x86-64_Ubuntu.tar.gz' 'VERSION_SPECIFIC_LINK_FROM_SEAFILE_CUSTOMER_CENTER'
We use Seafile version 12.0.6 as an example in the remainder of these instructions.
Uncompressing the package¶
The install package is downloaded as a compressed tarball which needs to be uncompressed.
Uncompress the package using tar:
# Debian/Ubuntu
tar xf seafile-pro-server_12.0.6_x86-64_Ubuntu.tar.gz
Now you have:
$ tree -L 2 /opt/seafile
.
├── seafile-license.txt
├── python-venv # you will not see this directory if you use ubuntu 22/debian 10
│ ├── bin
│ ├── include
│ ├── lib
│ ├── lib64 -> lib
│ └── pyvenv.cfg
├── seafile-pro-server-12.0.6
│ ├── check_init_admin.py
│ ├── index_op.py
│ ├── migrate-repo.py
│ ├── migrate-repo.sh
│ ├── migrate.py
│ ├── migrate.sh
│ ├── migrate_ldapusers.py
│ ├── parse_seahub_db.py
│ ├── pro
│ ├── remove-objs.py
│ ├── remove-objs.sh
│ ├── reset-admin.sh
│ ├── run_index_master.sh
│ ├── run_index_worker.sh
│ ├── runtime
│ ├── seaf-backup-cmd.py
│ ├── seaf-backup-cmd.sh
│ ├── seaf-encrypt.sh
│ ├── seaf-fsck.sh
│ ├── seaf-fuse.sh
│ ├── seaf-gc.sh
│ ├── seaf-import.sh
│ ├── seafile
│ ├── seafile-background-tasks.sh
│ ├── seafile-monitor.sh
│ ├── seafile.sh
│ ├── seahub
│ ├── seahub.sh
│ ├── setup-seafile-mysql.py
│ ├── setup-seafile-mysql.sh
│ ├── setup-seafile.sh
│ ├── sql
│ └── upgrade
└── seafile-pro-server_12.0.6_x86-64_Ubuntu.tar.gz
Tip
The names of the install packages differ for Seafile CE and Seafile PE. Using Seafile CE and Seafile PE 12.0.6 as an example, the names are as follows:
- Seafile CE:
seafile-server_12.0.6_x86-86.tar.gz; uncompressing into folderseafile-server-12.0.6 - Seafile PE:
seafile-pro-server_12.0.6_x86-86.tar.gz; uncompressing into folderseafile-pro-server-12.0.6
Setting up Seafile Pro databases¶
The install package comes with a script that sets Seafile up for you. Specifically, the script creates the required directories and extracts all files in the right place. It can also create a MySQL user and the three databases that Seafile's components require:
- ccnet server
- seafile server
- seahub
While ccnet server was merged into the seafile-server in Seafile 8.0, the corresponding database is still required for the time being
Run the script as user seafile:
Note
For installations using python virtual environment, activate it if it isn't already active
source python-venv/bin/activate
cd seafile-pro-server-12.0.6
./setup-seafile-mysql.sh
Configure your Seafile Server by specifying the following three parameters:
| Option | Description | Note |
|---|---|---|
| server name | Name of the Seafile Server | 3-15 characters, only English letters, digits and underscore ('_') are allowed |
| server's ip or domain | IP address or domain name used by the Seafile Server | Seafile client program will access the server using this address |
| fileserver port | TCP port used by the Seafile fileserver | Default port is 8082, it is recommended to use this port and to only change it if is used by other service |
In the next step, choose whether to create new databases for Seafile or to use existing databases. The creation of new databases requires the root password for the SQL server.
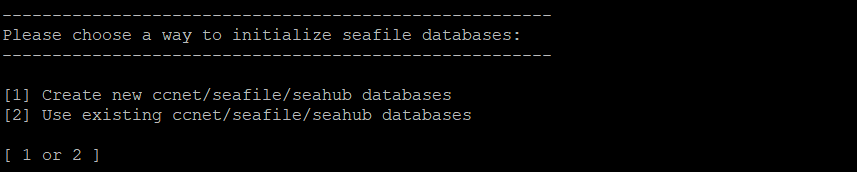
Note
If you don't have the root password, you need someone who has the privileges, e.g., the database admin, to create the three databases required by Seafile, as well as a MySQL user who can access the databases. For example, to create three databases ccnet_db / seafile_db / seahub_db for ccnet/seafile/seahub respectively, and a MySQL user "seafile" to access these databases run the following SQL queries:
create database `ccnet_db` character set = 'utf8';
create database `seafile_db` character set = 'utf8';
create database `seahub_db` character set = 'utf8';
create user 'seafile'@'localhost' identified by 'seafile';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON `ccnet_db`.* to `seafile`@localhost;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON `seafile_db`.* to `seafile`@localhost;
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON `seahub_db`.* to `seafile`@localhost;
The script creates these databases and a MySQL user that Seafile Server will use to access them. To this effect, you need to answer these questions:
| Question | Description | Note |
|---|---|---|
| mysql server host | Host address of the MySQL server | Default is localhost |
| mysql server port | TCP port used by the MySQL server | Default port is 3306; almost every MySQL server uses this port |
| mysql root password | Password of the MySQL root account | The root password is required to create new databases and a MySQL user |
| mysql user for Seafile | MySQL user created by the script, used by Seafile's components to access the databases | Default is seafile; the user is created unless it exists |
| mysql password for Seafile user | Password for the user above, written in Seafile's config files | Percent sign ('%') is not allowed |
| database name | Name of the database used by ccnet | Default is "ccnet_db", the database is created if it does not exist |
| seafile database name | Name of the database used by Seafile | Default is "seafile_db", the database is created if it does not exist |
| seahub database name | Name of the database used by seahub | Default is "seahub_db", the database is created if it does not exist |
The prompts you need to answer:
| Question | Description | Note |
|---|---|---|
| mysql server host | Host address of the MySQL server | Default is localhost |
| mysql server port | TCP port used by MySQL server | Default port is 3306; almost every MySQL server uses this port |
| mysql user for Seafile | User used by Seafile's components to access the databases | The user must exists |
| mysql password for Seafile user | Password for the user above | |
| ccnet database name | Name of the database used by ccnet, default is "ccnet_db" | The database must exist |
| seafile database name | Name of the database used by Seafile, default is "seafile_db" | The database must exist |
| seahub dabase name | Name of the database used by Seahub, default is "seahub_db" | The database must exist |
If the setup is successful, you see the following output:
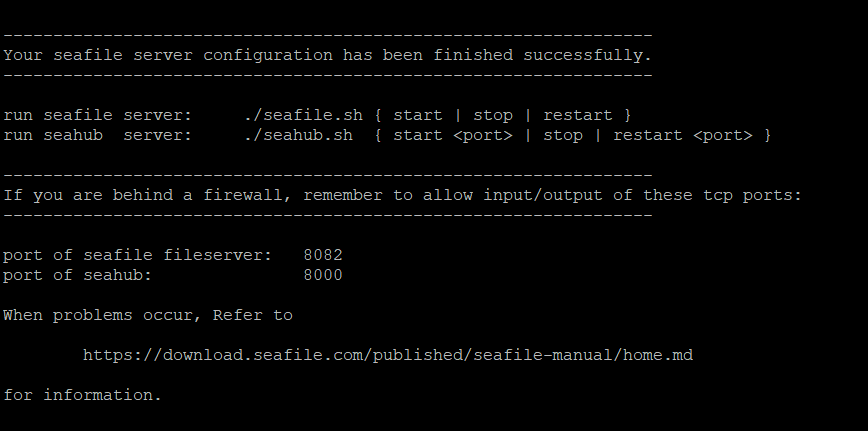
The directory layout then looks as follows:
/opt/seafile
├── seafile-license.txt
├── ccnet
├── conf
│ ├── gunicorn.conf.py
│ ├── seafdav.conf
│ ├── seafevents.conf
│ ├── seafile.conf
│ └── seahub_settings.py
├── pro-data
├── python-venv # you will not see this directory if you use ubuntu 22/debian 10
│ ├── bin
│ ├── include
│ ├── lib
│ ├── lib64 -> lib
│ └── pyvenv.cfg
├── seafile-data
│ └── library-template
├── seafile-pro-server-12.0.6
│ ├── check_init_admin.py
│ ├── index_op.py
│ ├── migrate-repo.py
│ ├── migrate-repo.sh
│ ├── migrate.py
│ ├── migrate.sh
│ ├── migrate_ldapusers.py
│ ├── parse_seahub_db.py
│ ├── pro
│ ├── remove-objs.py
│ ├── remove-objs.sh
│ ├── reset-admin.sh
│ ├── run_index_master.sh
│ ├── run_index_worker.sh
│ ├── runtime
│ ├── seaf-backup-cmd.py
│ ├── seaf-backup-cmd.sh
│ ├── seaf-encrypt.sh
│ ├── seaf-fsck.sh
│ ├── seaf-fuse.sh
│ ├── seaf-gc.sh
│ ├── seaf-import.sh
│ ├── seafile
│ ├── seafile-background-tasks.sh
│ ├── seafile-monitor.sh
│ ├── seafile.sh
│ ├── seahub
│ ├── seahub.sh
│ ├── setup-seafile-mysql.py
│ ├── setup-seafile-mysql.sh
│ ├── setup-seafile.sh
│ ├── sql
│ └── upgrade
├── seafile-pro-server_12.0.6_x86-64_Ubuntu.tar.gz
├── seafile-server-latest -> seafile-pro-server-12.0.6
└── seahub-data
└── avatars
The folder seafile-server-latest is a symbolic link to the current Seafile Server folder. When later you upgrade to a new version, the upgrade scripts update this link to point to the latest Seafile Server folder.
Setup Memory Cache¶
Memory cache is mandatory for pro edition. You may use Memcached or Reids as cache server.
Use the following commands to install memcached and corresponding libraies on your system:
# on Debian/Ubuntu 18.04+
apt-get install memcached libmemcached-dev -y
pip3 install --timeout=3600 pylibmc django-pylibmc
systemctl enable --now memcached
Add or modify the following configuration to seahub_settings.py:
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django_pylibmc.memcached.PyLibMCCache',
'LOCATION': '127.0.0.1:11211',
},
}
Add or modify the following configuration to seafile.conf:
[memcached]
memcached_options = --SERVER=127.0.0.1 --POOL-MIN=10 --POOL-MAX=100
Redis is supported since version 11.0
-
Install Redis with package installers in your OS.
-
Refer to Django's documentation about using Redis cache to add Redis configurations to
seahub_settings.py. -
Add or modify the following configuration to
seafile.conf:[redis] redis_host = 127.0.0.1 redis_port = 6379 max_connections = 100
Enabling HTTP/HTTPS (Optional but Recommended)¶
You need at least setup HTTP to make Seafile's web interface work. This manual provides instructions for enabling HTTP/HTTPS for the two most popular web servers and reverse proxies (e.g., Nginx).
Create the .env file in conf/ directory¶
nano /opt/seafile/conf/.env
Tip
JWT_PRIVATE_KEY, A random string with a length of no less than 32 characters can be generated from:
pwgen -s 40 1
JWT_PRIVATE_KEY=<Your jwt private key>
SEAFILE_SERVER_PROTOCOL=https
SEAFILE_SERVER_HOSTNAME=seafile.example.com
SEAFILE_MYSQL_DB_HOST=<your database host>
SEAFILE_MYSQL_DB_PORT=3306
SEAFILE_MYSQL_DB_USER=seafile
SEAFILE_MYSQL_DB_PASSWORD=<your MySQL password>
SEAFILE_MYSQL_DB_CCNET_DB_NAME=ccnet_db
SEAFILE_MYSQL_DB_SEAFILE_DB_NAME=seafile_db
SEAFILE_MYSQL_DB_SEAHUB_DB_NAME=seahub_db
Starting Seafile Server¶
Run the following commands in /opt/seafile/seafile-server-latest:
Note
For installations using python virtual environment, activate it if it isn't already active
source python-venv/bin/activate
su seafile
./seafile.sh start # Start Seafile service
./seahub.sh start # Start seahub website, port defaults to 127.0.0.1:8000
Success
The first time you start Seahub, the script prompts you to create an admin account for your Seafile Server. Enter the email address of the admin user followed by the password, i.e.:
What is the email for the admin account?
[ admin email ] <please input your admin's email>
What is the password for the admin account?
[ admin password ] <please input your admin's password>
Enter the password again:
[ admin password again ] <please input your admin's password again>
Now you can access Seafile via the web interface at the host address (e.g., https://seafile.example.com).
Enabling full text search¶
Seafile uses the indexing server ElasticSearch to enable full text search.
Deploying ElasticSearch¶
Our recommendation for deploying ElasticSearch is using Docker. Detailed information about installing Docker on various Linux distributions is available at Docker Docs.
Seafile PE 9.0 only supports ElasticSearch 7.x. Seafile PE 10.0, 11.0, 12.0 only supports ElasticSearch 8.x.
We use ElasticSearch version 8.15.0 as an example in this section. Version 8.15.0 and newer version have been successfully tested with Seafile.
Pull the Docker image:
sudo docker pull elasticsearch:8.15.0
Create a folder for persistent data created by ElasticSearch and change its permission:
sudo mkdir -p /opt/seafile-elasticsearch/data && chmod -R 777 /opt/seafile-elasticsearch/data/
Now start the ElasticSearch container using the docker run command:
sudo docker run -d \
--name es \
-p 9200:9200 \
-e "discovery.type=single-node" -e "bootstrap.memory_lock=true" \
-e "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms2g -Xmx2g" -e "xpack.security.enabled=false" \
--restart=always \
-v /opt/seafile-elasticsearch/data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data \
-d elasticsearch:8.15.0
Security notice
We sincerely thank Mohammed Adel of Safe Decision Co., for the suggestion of this notice.
By default, Elasticsearch will only listen on 127.0.0.1, but this rule may become invalid after Docker exposes the service port, which will make your Elasticsearch service vulnerable to attackers accessing and extracting sensitive data due to exposure to the external network. We recommend that you manually configure the Docker firewall, such as
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -s <your seafile server ip> --dport 9200 -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 9200 -j DROP
The above command will only allow the host where your Seafile service is located to connect to Elasticsearch, and other addresses will be blocked. If you deploy Elasticsearch based on binary packages, you need to refer to the official document to set the address that Elasticsearch binds to.
Modifying seafevents¶
Add the following configuration to seafevents.conf:
[INDEX FILES]
es_host = <your elasticsearch server's IP, e.g., 127.0.0.1> # IP address of ElasticSearch host
es_port = 9200 # port of ElasticSearch host
Finally, restart Seafile:
su seafile
./seafile.sh restart && ./seahub.sh restart