Seafile Docker Cluster Deployment¶
Architecture¶
The Seafile cluster solution employs a 3-tier architecture:
- Load balancer tier: Distribute incoming traffic to Seafile servers. HA (high availability) can be achieved by deploying multiple load balancer instances.
- Seafile server cluster: a cluster of Seafile server instances. If one instance fails, the load balancer will stop handing traffic to it. So HA is achieved.
- Backend storage: Distributed storage cluster, e.g. S3, Openstack Swift or Ceph.
This architecture scales horizontally. That means, you can handle more traffic by adding more machines. The architecture is visualized in the following picture.
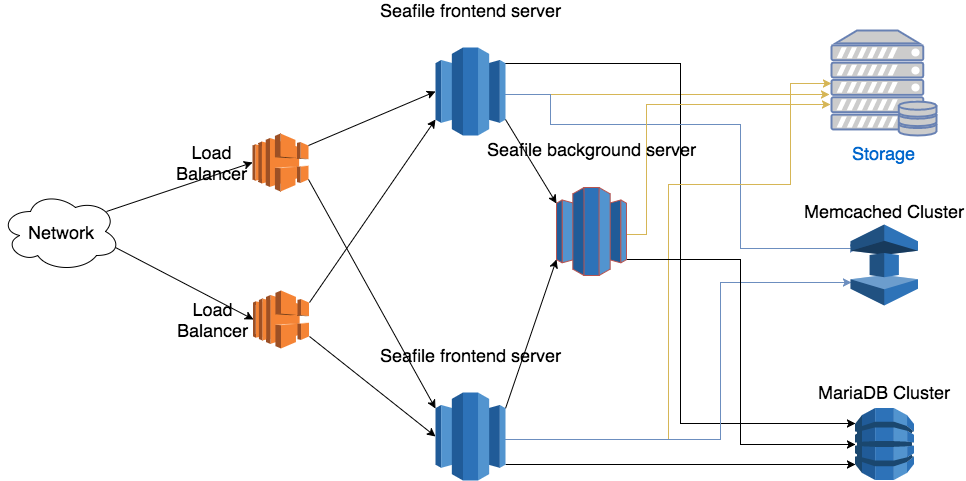
There are two main components on the Seafile server node: web server (Nginx/Apache) and Seafile app server. The web server passes requests from the clients to Seafile app server. The Seafile app servers work independently. They don't know about each other's state. That means each app server can fail independently without affecting other app server instances. The load balancer is responsible for detecting failure and re-routing requests.
Even though Seafile app servers work independently, they still have to share some session information. All shared session information is stored in memory cache. Thus, all Seafile app servers have to connect to the same memory cache server (cluster). Since Pro Edition 11.0, both memcached and Redis can be used as memory cache. Before 11.0, only memcached is supported. More details about memory cache configuration is available later.
The background server is the workhorse for various background tasks, including full-text indexing, office file preview, virus scanning, LDAP syncing. It should usually be run on a dedicated server for better performance. Currently only one background task server can be running in the entire cluster. If more than one background servers are running, they may conflict with each others when doing some tasks. If you need HA for background task server, you can consider using Keepalived to build a hot backup for it.
In the seafile cluster, only one server should run the background tasks, including:
- indexing files for search
- email notification
- LDAP sync
- virus scan
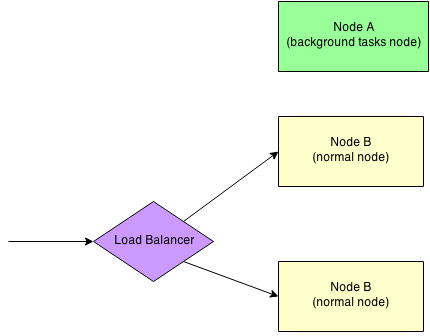
Let's assume you have three nodes in your cluster: A, B, and C.
- Node A is backend node that run background tasks.
- Node B and C are frontend nodes that serving requests from clients.
Cluster requirements¶
Please refer here for the details about the cluster requirements for all nodes in Seafile cluster. In general, we recommend that each node should have at least 2G RAM and a 2-core CPU (> 2GHz).
Deploy Seafile service¶
Deploy the first Seafile frontend node¶
-
Create the mount directory
mkdir -p /opt/seafile/shared -
Pulling Seafile image
docker pull seafileltd/seafile-pro-mc:12.0-latest -
Download the
seafile-server.ymland.envwget -O .env https://manual.seafile.com/12.0/repo/docker/cluster/env wget https://manual.seafile.com/12.0/repo/docker/cluster/seafile-server.yml -
Modify the variables in
.env(especially the terms like<...>).Tip
If you have already deployed S3 storage backend and plan to apply it to Seafile cluster, you can modify the variables in
.envto set them synchronously during initialization. -
Pleace license file
If you have a
seafile-license.txtlicense file, simply put it in the volume of the Seafile container. The volumne's default path in the Compose file is/opt/seafile/shared. If you have modified the path, save the license file under your custom path.If the license file has a different name or cannot be read, Seafile server will start with in trailer mode with most THREE users
-
Start the Seafile docker
docker compose up -dCluster init mode
Because
CLUSTER_INIT_MODEis true in the.envfile, Seafile docker will be started in init mode and generate configuration files. As the results, you can see the following lines if you trace the Seafile container (i.e.,docker logs seafile):--------------------------------- This is your configuration --------------------------------- server name: seafile server ip/domain: seafile.example.com seafile data dir: /opt/seafile/seafile-data fileserver port: 8082 database: create new ccnet database: ccnet_db seafile database: seafile_db seahub database: seahub_db database user: seafile Generating seafile configuration ... done Generating seahub configuration ... ----------------------------------------------------------------- Your seafile server configuration has been finished successfully. ----------------------------------------------------------------- [2024-11-21 02:22:37] Updating version stamp Start init Init success -
In initialization mode, the service will not be started. During this time you can check the generated configuration files (e.g., MySQL, Memcached, Elasticsearch) in configuration files:
-
After initailizing the cluster, the following fields can be removed in
.envCLUSTER_INIT_MODE, must be removed from.envfileCLUSTER_INIT_MEMCACHED_HOSTCLUSTER_INIT_ES_HOSTCLUSTER_INIT_ES_PORTINIT_S3_STORAGE_BACKEND_CONFIGINIT_S3_COMMIT_BUCKETINIT_S3_FS_BUCKETINIT_S3_BLOCK_BUCKETINIT_S3_KEY_IDINIT_S3_SECRET_KEY
Tip
We recommend that you check that the relevant configuration files are correct and copy the
SEAFILE_VOLUMEdirectory before the service is officially started, because only the configuration files are generated after initialization. You can directly migrate the entire copiedSEAFILE_VOLUMEto other nodes later:cp -r /opt/seafile/shared /opt/seafile/shared-bak -
Restart the container to start the service in frontend node
docker compose down docker compose up -dFrontend node starts successfully
After executing the above command, you can trace the logs of container
seafile(i.e.,docker logs seafile). You can see the following message if the frontend node starts successfully:*** Running /etc/my_init.d/01_create_data_links.sh... *** Booting runit daemon... *** Runit started as PID 20 *** Running /scripts/enterpoint.sh... 2024-11-21 03:02:35 Nginx ready 2024-11-21 03:02:35 This is an idle script (infinite loop) to keep container running. --------------------------------- Seafile cluster frontend mode --------------------------------- Starting seafile server, please wait ... Seafile server started Done. Starting seahub at port 8000 ... Seahub is started Done.
Deploy the others Seafile frontend nodes¶
-
Create the mount directory
$ mkdir -p /opt/seafile/shared -
Pull Seafile image
-
Copy
seafile-server.yml,.envand configuration files from the first frontend node -
Start the service
docker compose up -d
Deploy seafile backend node¶
-
Create the mount directory
$ mkdir -p /opt/seafile/shared -
Pull Seafile image
-
Copy
seafile-server.yml,.envand configuration files from frontend nodeNote
The configuration files from frontend node have to be put in the same path as the frontend node, i.e.,
/opt/seafile/shared/seafile/conf/* -
Modify
.env, setCLUSTER_MODEtobackend -
Start the service in the backend node
docker compose up -dBackend node starts successfully
After executing the above command, you can trace the logs of container
seafile(i.e.,docker logs seafile). You can see the following message if the backend node starts successfully:*** Running /etc/my_init.d/01_create_data_links.sh... *** Booting runit daemon... *** Runit started as PID 21 *** Running /scripts/enterpoint.sh... 2024-11-21 03:11:59 Nginx ready 2024-11-21 03:11:59 This is an idle script (infinite loop) to keep container running. --------------------------------- Seafile cluster backend mode --------------------------------- Starting seafile server, please wait ... Seafile server started Done. Starting seafile background tasks ... Done.
Deploy load balance (Optional)¶
Note
Since Seafile Pro server 6.0.0, cluster deployment requires "sticky session" settings in the load balancer. Otherwise sometimes folder download on the web UI can't work properly. Read the "Load Balancer Setting" section below for details
Generally speaking, in order to better access the Seafile service, we recommend that you use a load balancing service to access the Seafile cluster and bind your domain name (such as seafile.cluster.com) to the load balancing service. Usually, you can use:
- Cloud service provider's load balancing service (e.g., AWS Elastic Load Balancer)
-
Deploy your own load balancing service, our document will give two of common load balance services:
- Nginx
- HAproxy
AWS Elastic Load Balancer (ELB)¶
In the AWS ELB management console, after you've added the Seafile server instances to the instance list, you should do two more configurations.
First you should setup HTTP(S) listeners. Ports 443 and 80 of ELB should be forwarded to the ports 80 or 443 of the Seafile servers.
Then you setup health check
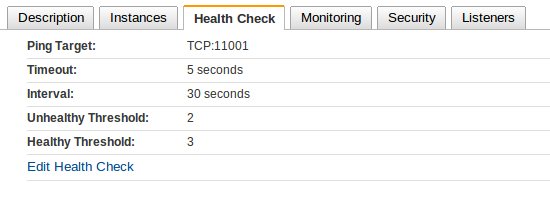
Refer to AWS documentation about how to setup sticky sessions.
Nginx¶
-
Install Nginx in the host if you would like to deploy load balance service
sudo apt update sudo apt install nginx -
Create the configurations file for Seafile cluster
sudo nano /etc/nginx/sites-available/seafile-clusterand, add the following contents into this file:
upstream seafile_cluster { server <IP: your frontend node 1>:80; server <IP: your frontend node 2>:80; ... } server { listen 80; server_name <your domain>; location / { proxy_pass http://seafile_cluster; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme; http_502 http_503 http_504; } } -
Link the configurations file to
sites-enableddirectory:sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/seafile-cluster /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ -
Test and enable configuration
sudo nginx -t sudo nginx -s reload
HAproxy and Keepalived services¶
Execute the following commands on the two Seafile frontend servers:
$ apt install haproxy keepalived -y
$ mv /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg.bak
$ cat > /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg << 'EOF'
global
log 127.0.0.1 local1 notice
maxconn 4096
user haproxy
group haproxy
defaults
log global
mode http
retries 3
timeout connect 10000
timeout client 300000
timeout server 36000000
listen seafile 0.0.0.0:80
mode http
option httplog
option dontlognull
option forwardfor
cookie SERVERID insert indirect nocache
server seafile01 Front-End01-IP:8001 check port 11001 cookie seafile01
server seafile02 Front-End02-IP:8001 check port 11001 cookie seafile02
EOF
Warning
Please correctly modify the IP address (Front-End01-IP and Front-End02-IP) of the frontend server in the above configuration file. Other wise it cannot work properly.
Choose one of the above two servers as the master node, and the other as the slave node.
Perform the following operations on the master node:
$ cat > /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf << 'EOF'
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
notification_email {
root@localhost
}
notification_email_from keepalived@localhost
smtp_server 127.0.0.1
smtp_connect_timeout 30
router_id node1
vrrp_mcast_group4 224.0.100.18
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state MASTER
interface eno1 # Set to the device name of a valid network interface on the current server, and the virtual IP will be bound to the network interface
virtual_router_id 50
priority 100
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass seafile123
}
virtual_ipaddress {
172.26.154.45/24 dev eno1 # Configure to the correct virtual IP and network interface device name
}
}
EOF
Warning
Please correctly configure the virtual IP address and network interface device name in the above file. Other wise it cannot work properly.
Perform the following operations on the standby node:
$ cat > /etc/keepalived/keepalived.conf << 'EOF'
! Configuration File for keepalived
global_defs {
notification_email {
root@localhost
}
notification_email_from keepalived@localhost
smtp_server 127.0.0.1
smtp_connect_timeout 30
router_id node2
vrrp_mcast_group4 224.0.100.18
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state BACKUP
interface eno1 # Set to the device name of a valid network interface on the current server, and the virtual IP will be bound to the network interface
virtual_router_id 50
priority 98
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass seafile123
}
virtual_ipaddress {
172.26.154.45/24 dev eno1 # Configure to the correct virtual IP and network interface device name
}
}
EOF
Finally, run the following commands on the two Seafile frontend servers to start the corresponding services:
$ systemctl enable --now haproxy
$ systemctl enable --now keepalived
So far, Seafile cluster has been deployed.
HTTPS¶
You can engaged HTTPS in your load balance service, as you can use certificates manager (e.g., Certbot) to acquire and enable HTTPS to your Seafile cluster. You have to modify the relative URLs from the prefix http:// to https:// in seahub_settings.py and .env, after enabling HTTPS.
(Optional) Deploy SeaDoc server¶
You can follow here to deploy SeaDoc server. And then modify SEADOC_SERVER_URL in your .env file